Flame cutting and plasma cutting
Flame cutting and plasma cutting
There is a wide range of methods used to cut metals. These include laser cutting, mechanical cutting, water jet, and many more. In this article, we will review plasma cutting and flame cutting, also known as oxygen burning or oxy-fuel cutting. These cutting methods, along with laser cutting, fall into the category of thermal cutting.
In flame cutting systems, metal is pre-heated by burning the fuel as to the temperature of its ignition in oxygen. A jet of pure oxygen is then directed onto the pre-heated area creating a chemical reaction of metal oxidation. The resulting oxide and molten metal are then blown away by the high-powered oxygen jet. The cut quality depends on the cutting speed and the choice of the fuel gas. This method has several advantages. It is low in capital costs and is inexpensive to run. It is highly portable and versatile: the sample torches can be used for cutting, welding, brazing, and soldering. There are also no electrical requirements. This method is particularly suited for cutting metal slabs as thick as one meter. It is limited, however, to mild and low alloy steels and is less suitable for aluminum, cast iron, or stainless steel. As cutting thick metal slabs takes time, fabricators greatly benefit from the automation of this cutting process such as integration with a CNC system.
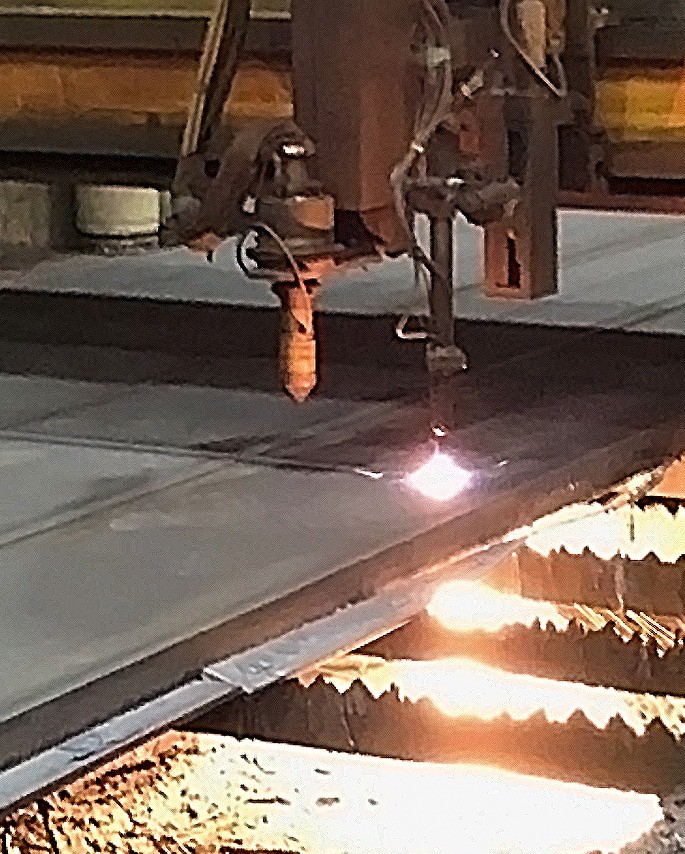 Plasma cutting, on the other hand, is suitable for many types of metals and is an efficient method for cutting thin as well as thick, up to tens of centimeters, metal plates. In plasma cutters, an initial low energy electric arc between an electrode and the plasma cutter nozzle is used to create plasma by partially ionizing a compressed gas, which is blown at a high speed through a nozzle forming a plasma jet. This plasma jet transfers the initial arc to a grounded electrically conductive material to be cut thereby making it part of the main circuit. The electricity traveling down the transferred arc creates a plasma channel and initiates the main arc which serves as a heat source and does the cutting. Concurrently, the high-speed plasma jet blows the molten material away. Taking advantage of high-quality cuts produced by this process, some manufacturers make CNC plasma tables enabling high precision cutting, not far off from the laser cutting. Although plasma cutting requires occasional replacement of the electrode and the plasma cutter nozzle, it is inexpensive to run due to the low cost of the cutting gas often being compressed air.
Plasma cutting, on the other hand, is suitable for many types of metals and is an efficient method for cutting thin as well as thick, up to tens of centimeters, metal plates. In plasma cutters, an initial low energy electric arc between an electrode and the plasma cutter nozzle is used to create plasma by partially ionizing a compressed gas, which is blown at a high speed through a nozzle forming a plasma jet. This plasma jet transfers the initial arc to a grounded electrically conductive material to be cut thereby making it part of the main circuit. The electricity traveling down the transferred arc creates a plasma channel and initiates the main arc which serves as a heat source and does the cutting. Concurrently, the high-speed plasma jet blows the molten material away. Taking advantage of high-quality cuts produced by this process, some manufacturers make CNC plasma tables enabling high precision cutting, not far off from the laser cutting. Although plasma cutting requires occasional replacement of the electrode and the plasma cutter nozzle, it is inexpensive to run due to the low cost of the cutting gas often being compressed air.
Useful links:
https://www.eworldtrade.com/c/plazmamaxcompany/